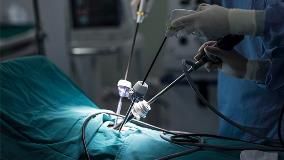










Cytoreductive surgery refers to surgical procedures aimed at reducing the volume of malignant tumors in the abdominal and pelvic organs.
These operations are indicated in cases of widespread cancer within the abdominal cavity, regardless of the primary tumor site, with the goal of achieving maximum tumor mass removal.
For patients with ovarian malignancies, the standard treatment involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy. Surgery is prioritized as an independent treatment method and as the most crucial stage within a comprehensive therapeutic approach.
Primary cytoreductive surgery is the standard treatment for advanced ovarian cancer, particularly in stage III. The objective is to reduce or completely eliminate macroscopic tumor masses to the greatest extent possible. The role of cytoreductive surgery in stage IV (according to FIGO) is debated; however, it is believed that patients with isolated pleural effusion, supraclavicular lymph nodes, or a solitary skin metastasis may be treated similarly to stage III.
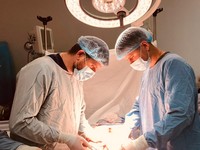
Cytoreductive surgeries should always be performed in specialized oncology centers where it is possible to involve a team of highly qualified specialists who are experts in conducting extensive surgical interventions. Surgeries performed outside an oncological facility significantly increase the risk of disease progression, postoperative complications, and result in lower recurrence-free and overall survival rates compared to patients operated on in an oncology hospital.
Preparation for cytoreductive surgery is always individualized and involves a more extensive list of examinations than for patients with benign conditions.