

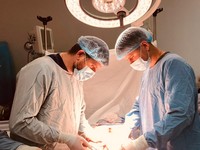








Laparoscopic radical surgeries are modern, minimally invasive surgical treatments used for the removal of malignant tumors. This type of surgery involves making several small incisions in the abdominal wall through which specialized instruments and a camera are inserted, allowing the surgeon to monitor the procedure on a screen in real-time.
One of the main advantages of laparoscopic radical surgeries is minimal tissue trauma.
This results in faster recovery for the patient, reduced postoperative pain, and a lower risk of complications such as infections or adhesions. Patients undergoing these surgeries typically spend less time in the hospital and can return to their normal lives more quickly.
Laparoscopic radical surgeries are used in the treatment of various cancers, such as ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer, and others. Beyond oncological surgeries, laparoscopy is also employed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in cases of benign tumors and other abdominal conditions.
However, not all patients are candidates for laparoscopic surgeries. In cases of very large tumors or advanced disease stages, laparoscopy may be technically challenging or ineffective. In such instances, traditional open surgery is recommended.
Laparoscopic radical surgeries are a powerful tool in modern surgery, allowing for effective radical tumor removal while minimizing tissue trauma and promoting faster patient recovery.